Whether you’re sipping on a diet soda, reaching for a low-calorie snack, or sweetening your coffee with a sugar substitute, knowing more about these products is essential to making informed health choices.
What are Artificial Sweeteners?
Artificial sweeteners are man-made sugar substitutes that are often much sweeter than regular sugar, but contain little or no calories. Common ones include:
- Aspartame (brand name Equal): found in products like Diet Coke
- Sucralose (brand name Splenda): found in baked goods, drinks, and more
- Saccharin (brand name Sweet’N Low): found in processed foods, canned or preserved fruits, and more
- Acesulfame potassium (Ace-K): less common, often used in baked goods and soft drinks like Pepsi products
- Steviol glycosides (Stevia): extracted from the stevia plant, often found in herbal teas, protein powders and some sodas
- Monkfruit: natural sweetener extracted from a Chinese fruit called Luo Han Guo and is used in baked goods, drinks, and more
Here is an FDA chart comparing the levels of sweetness among artificial sweeteners compared to table sugar:
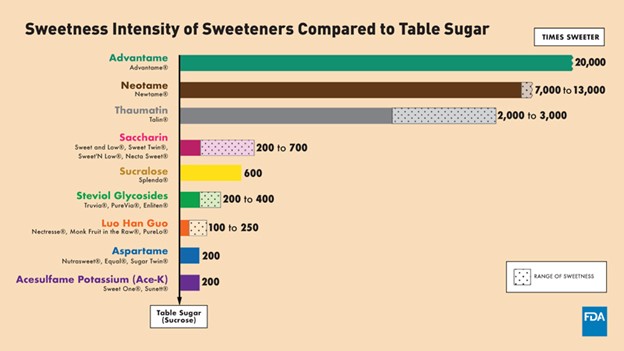
Artificial sweeteners are used in various foods and beverages to reduce calorie intake, aid in weight loss, and manage blood sugar levels for people with diabetes. But what’s the catch? First, let’s look at the benefits and then the controversies surrounding these sweeteners.
The Potential Benefits of Artificial Sweeteners
- Calorie Control: Artificial sweeteners can help to limit calorie consumption. For instance, swapping sugary drinks for diet versions can significantly cut down on daily sugar intake.
- Blood Sugar Management: For those living with diabetes, artificial sweeteners can provide a way to enjoy sweet flavors without affecting blood glucose levels. If you have diabetes, be mindful that some of the artificial sugar packets (Splenda) may have dextrose; which depending on the amount used, can raise your blood sugar.
- Reduced Risk of Tooth Decay: Unlike sugar, artificial sweeteners do not create cavities and don’t contribute to tooth decay.
- Weight Management: Some studies may suggest that replacing sugary foods and beverages with low-calorie options may help with weight loss and weight maintenance.
Why are Artificial Sweeteners Controversial?
Despite the benefits, artificial sweeteners have come under scrutiny, and various controversies hover around their safety and health effects. Some common concerns people have with artificial sweeteners:
Health Risk
In the past, some artificial sweeteners, particularly saccharin, were linked to cancer due to early animal studies. However, the FDA declared saccharin safe in 2000, and the research indicates that it does not pose a cancer risk to humans. More recent studies have pointed out that most artificial sweeteners, including aspartame and sucralose, are safe to consume in typical amounts. The Acceptable Daily Intake (ADI) for these sweeteners is set by the FDA and is often much higher than what most people consume.
Gut Health
Some studies suggest that consuming artificial sweeteners may alter the balance of healthy bacteria in the gut, potentially leading to metabolic changes. However, the evidence remains inconclusive, and more research is needed to understand the long-term effects fully.
Cravings and Overeating
Another controversy revolves around the idea that consuming artificial sweeteners may lead to increased cravings for sweet foods, potentially resulting in overeating. Some people find that using these products leads to a desire for other high-calorie foods. However, other studies indicate that when used correctly, they can assist with managing cravings. The key seems to be moderation.
Current Research and Guidelines
Artificial sweeteners are one of the most highly investigated additives on the planet . Research on artificial sweeteners remains ongoing, and findings often contradict each other, making it hard for consumers to navigate. Additionally, results found in animal studies do not always translate to humans. Here are some essential takeaways from current studies:
Generally Recognized as Safe
The FDA and WHO recognize artificial sweeteners as safe additives to our food supply, but there is mixed research on their long term benefits of weight loss.
Moderation is Key
Most health organizations, including the Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics and the American Diabetes Association, agree that moderate consumption of artificial sweeteners is safe for the general population.
Individual Preferences
People react differently to sweeteners, so it’s crucial to pay attention to your body. If you notice negative effects such as digestive issues or unusual cravings, it might be worth reevaluating your artificial sweetener intake.
Whole Foods First
Even if you are eating artificial sweeteners, odds are they are not making up the majority of your diet. Focusing on including whole foods like fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins into your diet is beneficial for overall health and wellness.
Here is a table from the FDA demonstrating how many servings of artificial sweetner packets are safe to eat in a day for someone who is 130 lb:
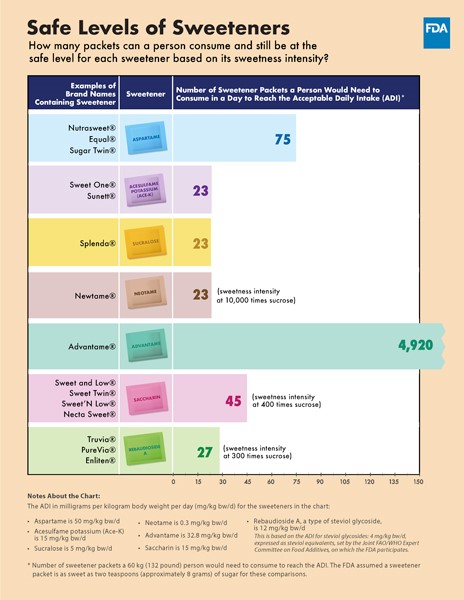
Artificial sweeteners can be a helpful tool for reducing sugar consumption, possibly managing weight, and controlling blood sugar levels. However, it’s essential to approach them with knowledge and care. Listen to your body, stay informed about the latest research, and focus on overall dietary patterns rather than fixating on single ingredients.
To learn more about different types of sugars and sweeteners, check out our handout on natural and non-nutritive sweeteners here.
Whether you enjoy a naturally sweetened beverage or opt for low-calorie snacks, understand that moderation is the best approach. If you have specific health concerns or conditions, consulting with a registered dietitian can help tailor your dietary choices to fit your needs. Call 919.237.1337 option 4, or visit here to set up an appointment with a dietitian .
Resources:
- https://nutritionsource.hsph.harvard.edu/2023/06/06/who-guidelines-non-sugar-sweeteners/
- https://www.mayoclinic.org/healthy-lifestyle/nutrition-and-healthy-eating/in-depth/artificial-sweeteners/art-20046936
- https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/artificial-sweeteners-good-or-bad#appetite-weight




